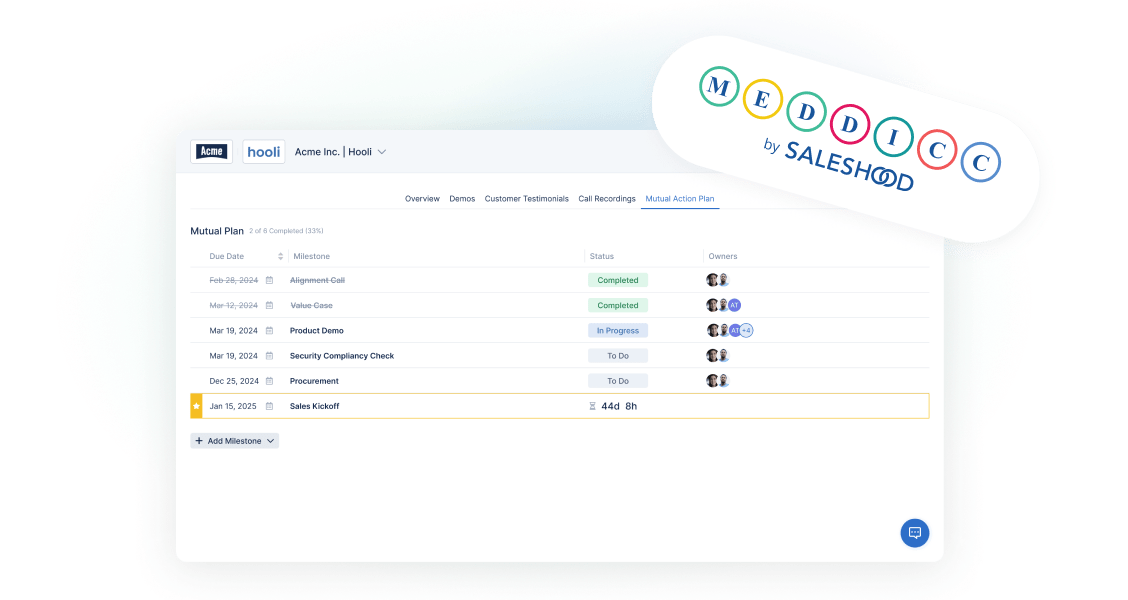
In B2B enterprise software sales, the path to closing a deal is often fraught with obstacles and uncertainties. This is where the MEDDICC framework helps, offering a structured approach to managing and progressing sales opportunities. Among the various tools and strategies integrated within MEDDICC, Mutual Action Plans (MAPs) stand out as particularly vital to mapping out a customer’s Decision Marking Process and Decision Criteria. This blog explores the importance of MAPs in the context of MEDDICC, explaining how they enhance sales effectiveness and contribute to successful win-win deal outcomes.
Understanding MEDDICC
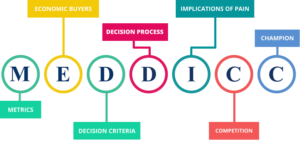
Before delving into the significance of Mutual Action Plans, it’s essential to grasp the MEDDICC framework. MEDDICC is an acronym that represents a set of criteria designed to qualify and manage sales opportunities. It stands for:
- Metrics: Quantifiable measures that define the value of the solution.
- Economic Buyer: The individual with the authority to make the purchasing decision.
- Decision Criteria: The standards the customer uses to evaluate potential solutions.
- Decision Process: The process the customer follows to make a purchasing decision.
- Identify Pain: The specific challenges or problems the customer is facing.
- Champion: An internal advocate who supports the solution and can influence the decision.
- Competition: The alternative solutions being considered by the customer.
MEDDICC helps sales teams systematically qualify leads, understand customer needs, and align their efforts with the customer’s decision-making process. However, to truly operationalize these criteria and ensure that both the sales team and the customer are on the same page, Mutual Action Plans become indispensable.
What is a Mutual Action Plan (MAP)?
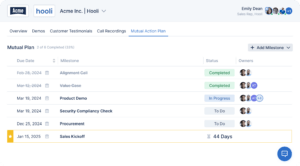
A Mutual Action Plan is a collaborative document that outlines the steps, responsibilities, and timelines for both the seller and the buyer to reach a successful deal closure. It serves as a roadmap, detailing the actions that need to be taken by each party to move the sales process forward. Typically, a MAP includes:
- Key Milestones: Critical stages of the sales process.
- Tasks and Deliverables: Specific actions required from both parties.
- Deadlines: Target dates for completing tasks.
- Responsibilities: Designated individuals accountable for each task.
 |
The Role of MAPs in MEDDICC
| Enhancing clarity and alignment |
| In complex sales environments, misunderstandings and misalignments can derail the sales process. A Mutual Action Plan ensures that both the seller and the buyer have a clear understanding of the steps involved and their respective roles. This alignment is crucial in MEDDICC, where understanding the customer’s decision criteria and process is fundamental. By establishing a shared roadmap, MAPs help ensure that both parties are working towards the same goals and timelines. |
| Facilitating accurate qualification |
| One of the core purposes of MEDDICC is to accurately qualify sales opportunities. MAPs play a crucial role in this by providing a structured way to validate the customer’s commitment and readiness to move forward. By agreeing to a MAP, the customer demonstrates their willingness to engage in a structured process, indicating a higher level of qualification. This helps sales teams focus their efforts on opportunities with a genuine potential for closure. With a MAP, sales managers improve forecasts accuracy and can gain better visibility into the progress of each deal. |
| Driving accountability |
| Accountability is a key component of any successful sales process. Mutual Action Plans explicitly outline the responsibilities of both the seller and the buyer, ensuring that each party is held accountable for their commitments. This is especially important in MEDDICC, where the involvement of the economic buyer, champion, and other stakeholders is crucial. By clearly defining who needs to do what and by when, MAPs help maintain momentum and prevent delays. |
| Building trust and collaboration |
| Trust is the cornerstone of any successful sales relationship. MAPs foster trust by promoting transparency and collaboration. When a sales team presents a MAP, it demonstrates their commitment to a structured, customer-centric approach. This transparency helps build credibility and trust with the customer, enhancing the overall relationship. In the context of MEDDICC, where a champion’s support and the economic buyer’s trust are essential, MAPs can be instrumental in building and maintaining these relationships. |
| Mitigating deal risks |
| Every sales opportunity comes with inherent risks. These can range from internal challenges within the customer’s organization to external competitive threats. MAPs help mitigate these risks by providing a proactive framework for identifying and addressing potential obstacles. For instance, by including steps to handle competitive evaluations or internal approvals, MAPs ensure that these risks are managed effectively. This aligns with MEDDICC’s focus on understanding and navigating the competitive landscape. |
| Driving deal urgency and momentum |
| Stalled deals are a common frustration in sales. MAPs help prevent stagnation by creating a sense of urgency and momentum. The clearly defined deadlines and responsibilities ensure that both parties are consistently working towards the next milestone. This continuous progress is crucial in the MEDDICC framework, where maintaining momentum through the decision process can be the difference between winning and losing a deal. |
Decision Making Process in MEDDICC
In the MEDDICC framework, Mutual Action Plans (MAPs) are most relevant to the “Decision Making Process” component. The “Decision Making Process” refers to the steps and stages the customer follows to make a purchasing decision. Understanding this process is crucial for sales teams to effectively guide the customer from initial interest to final purchase. It involves identifying all the decision-makers, the criteria they use, and the sequence of activities required to reach a decision.
Relevance of MAPs to the Decision Process
-
Clarifying steps and stages: A Mutual Action Plan outlines the specific steps and stages that both the seller and the buyer need to take. This directly correlates with understanding and mapping out the customer’s decision process. By jointly creating a MAP, the sales team can ensure that they are in sync with the customer’s internal steps, milestones, and approval processes.
-
Defining responsibilities and timelines: The MAP delineates the responsibilities of each party and sets clear timelines. This helps the sales team understand who the key stakeholders are, what their roles entail, and when critical actions need to be completed. This is essential for navigating the Decision Process, as it ensures that all necessary approvals and evaluations happen within the expected timeframe.
-
Ensuring alignment and progress: One of the primary purposes of a MAP is to ensure that both parties are aligned on the path forward and are making continuous progress. This alignment is crucial for the Decision Process, as it keeps the sales engagement on track, preventing delays and misunderstandings that could derail the sale.
-
Mitigating risks and objections: By proactively addressing potential risks and objections within the MAP, the sales team can better navigate the Decision Process. This preparation helps in anticipating and overcoming any hurdles that might arise, ensuring a smoother decision-making journey for the customer.
-
Building trust and commitment: A well-structured MAP demonstrates the seller’s commitment to a structured, transparent, and customer-centric approach. This builds trust with the customer, making them more likely to follow through with the Decision Process as outlined in the plan.
 |
Implementing MAPs in your sales process
To effectively integrate Mutual Action Plans within the MEDDICC framework, consider the following best practices:
- Early introduction: Introduce the concept of a MAP early in the sales process. This sets the expectation for a structured approach from the outset.
- Collaborative creation: Develop the MAP in collaboration with the customer. This ensures buy-in and alignment from both parties.
- Regular reviews: Schedule regular check-ins to review progress against the MAP. This helps maintain momentum and address any issues promptly.
- Flexibility: While structure is important, remain flexible and adaptable. Be prepared to adjust the MAP as circumstances evolve.
- Clear communication: Ensure that all stakeholders understand the MAP and their responsibilities. Clear communication is key to successful execution.
Conclusion
In the dynamic and competitive landscape of B2B enterprise sales, leveraging the MEDDICC framework can significantly enhance a sales team’s effectiveness. Within this framework, Mutual Action Plans serve as a vital tool, driving clarity, alignment, accountability, and progress. By integrating MAPs into your MEDDICC approach, you can better qualify opportunities, build stronger relationships, and ultimately increase your chances of closing deals successfully.